How Guar Gum Powder Controls Moisture Migration in Processed Foods?
Table of Contents
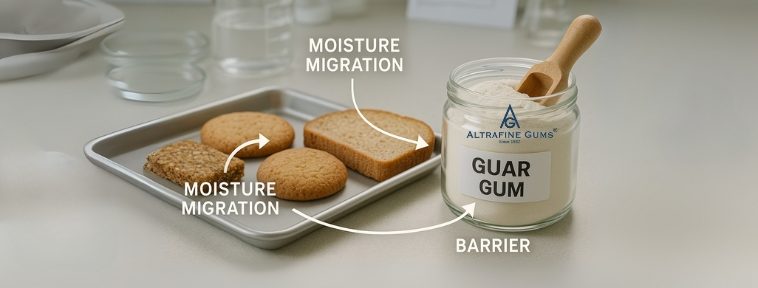
Moisture migration in processed foods refers to the movement of water from one part of the food to another, which can drastically affect the product’s quality and shelf life. This movement of moisture can occur due to various factors like temperature fluctuations, humidity and the natural composition of the food. In processed foods, moisture migration leads to issues like sogginess, drying or hardening, which can significantly compromise texture, taste and consumer satisfaction.
The causes of moisture migration are primarily physical in nature, often caused by the food’s ability to absorb or release water in response to environmental conditions. When moisture moves from high to low moisture content areas, it can lead to negative impacts such as the formation of a soggy product or the drying out of foods that were meant to retain moisture.
The effects of moisture migration on processed foods include:
- Texture Degradation: As moisture migrates, it can change the texture of the product, making it either too dry or too moist, which compromises the original feel and bite of the food.
- Reduced Shelf Life: Increased moisture can lead to microbial growth, which shortens the product’s shelf life, while excessive dryness may cause products to lose their appeal.
- Quality Issues: The overall quality of the food product deteriorates, impacting both the appearance and consumer satisfaction.
With these challenges, controlling moisture migration becomes essential in ensuring product consistency and consumer satisfaction over time.
Overview of Guar Gum Powder
Guar gum powder is a natural hydrocolloid derived from the endosperm of the guar bean, a legume primarily grown in arid regions of India and Pakistan. Guar gum has been widely recognized in the food industry due to its functional properties that contribute to the stability and quality of various food products.
Source and Composition of Guar Gum
The guar bean consists of three main components: endosperm, germ and husk. The endosperm, which contains the polysaccharide galactomannan, is the primary source of guar gum powder. Guar gum has a high molecular weight, making it highly effective in forming gels and acting as a thickener in food applications. It is primarily composed of galactose and mannose units, which are connected in a linear chain. This molecular structure allows guar gum to interact with water molecules and form highly viscous solutions, which is crucial for moisture control.
Functional Properties in Food Applications
Guar gum powder is widely used for its thickening, gelling and water-binding properties. In food, it helps improve texture, stabilize emulsions and prevent the separation of ingredients. Its ability to retain moisture makes it particularly valuable in controlling moisture migration in various food formulations.
- Thickening Agent: Guar gum can increase the viscosity of liquids, making it ideal for sauces, dressings and soups.
- Water Binder: Guar gum has an exceptional ability to bind water, which makes it effective in preventing moisture migration in food products.
- Stabilizing Agent: Guar gum helps maintain the stability of emulsions, preventing the separation of oil and water phases in food products like salad dressings and mayonnaise.
These functional properties make guar gum an essential ingredient in a variety of processed foods, particularly in applications where moisture retention and consistency are crucial.

Mechanism of Moisture Control by Guar Gum
Guar gum controls moisture migration in processed foods through its water-binding capacity, the formation of moisture barriers and its viscosity enhancement properties. The combination of these factors allows guar gum to maintain the desired texture and prevent moisture-related issues such as sogginess or dryness.
Water-Binding Capacity
Guar gum’s molecular structure allows it to bind large amounts of water through hydrogen bonding. This water-binding ability is essential in food applications because it ensures that moisture is retained within the food product and doesn’t migrate uncontrollably. By interacting with water molecules, guar gum forms a gel-like network, trapping moisture within the food matrix and preventing it from migrating to unwanted areas.
Formation of Moisture Barriers
In addition to binding water, Guar Gum Powder forms a protective moisture barrier on the surface of foods. This barrier reduces moisture loss, preserving the product’s texture and preventing the absorption of moisture from the environment. For example, in frozen foods, guar gum can prevent the formation of ice crystals that can lead to texture degradation and sogginess upon thawing.
Viscosity Enhancement and Gel Formation
Guar gum’s ability to increase the viscosity of food products enhances the overall texture and stability of processed foods. It forms gels when combined with water and this gel structure plays a crucial role in controlling moisture migration. The thicker consistency prevents excessive moisture movement, ensuring that the product remains in optimal condition during storage and handling.
Applications of Guar Gum in Moisture-Sensitive Processed Foods
Guar powder is widely utilized in various moisture-sensitive food products due to its ability to control moisture migration and maintain texture stability. Here are some examples of food applications where guar gum plays a significant role:
Baked Goods (Cakes, Cookies, Breads)
In baked goods, moisture migration can cause products to become either too dry or too soggy, impacting the final texture and mouthfeel. Guar gum powder helps maintain moisture balance by binding water, ensuring that the product retains its softness without becoming overly moist or dry.
- Cakes: Guar gum helps maintain moisture in cakes, preventing them from drying out and extending their shelf life.
- Cookies: By binding moisture, guar gum helps cookies retain their crisp texture without becoming overly hard.
- Breads: In bread products, guar gum contributes to moisture retention, resulting in a more consistent crumb texture and improved shelf life.
Frozen Foods
Frozen foods are highly susceptible to moisture migration due to temperature fluctuations during storage and thawing. Guar korma helps form a moisture barrier that prevents the loss of moisture during freezing and protects the texture of the food when it is thawed.
- Ice Cream: Guar gum is widely used in ice cream formulations to prevent ice crystal formation, ensuring smoothness and creaminess.
- Frozen Meals: For ready-to-eat frozen meals, guar gum helps maintain the consistency and texture, preventing the food from becoming too watery or soggy after reheating.
Dairy-Based Desserts and Ice Creams
In dairy-based desserts and ice creams, moisture control is critical to maintaining the desired texture. Guar gum powder acts as a stabilizer, preventing ice crystals from forming and ensuring a smooth, creamy texture. It also prevents the separation of water from other ingredients in frozen dairy products.
Ready-to-Eat Meals and Snacks
Ready-to-eat meals and snacks often face challenges related to moisture migration, which can lead to the loss of flavor and texture. Guar gum helps prevent excessive moisture loss or gain in these products, ensuring that they maintain their quality during storage.

Comparison with Other Hydrocolloids
While guar gum is highly effective in controlling moisture migration, it is important to compare it with other hydrocolloids such as xanthan gum and locust bean gum. These alternatives may offer similar functions but have different properties and applications.
Guar Gum vs. Xanthan Gum
Both guar gum and xanthan gum are used for their thickening and water-binding properties. However, guar gum has a higher water-binding capacity compared to xanthan gum, which makes it more effective in preventing moisture migration in foods. Additionally, guar gum is often more cost-effective, making it a preferred choice for large-scale food applications.
Guar Gum vs. Locust Bean Gum
Locust bean gum is another hydrocolloid used in food applications, often for its gelling properties. While both guar gum and locust bean gum can improve the texture of processed foods, guar churi is generally more efficient in controlling moisture migration due to its superior water-binding capacity.
Impact on Shelf Life and Texture Stability
One of the main reasons guar gum is widely used in processed foods is its ability to extend shelf life and maintain texture stability. By controlling moisture migration, guar gum helps prevent the product from becoming too soggy or dry, which can significantly affect the sensory qualities of the food.
Prevention of Sogginess or Dryness
For products like cakes, cookies and snacks, moisture migration can lead to sogginess or dryness, making them less enjoyable to consumers. Guar gum prevents these issues by maintaining the ideal moisture balance, ensuring that the texture remains consistent throughout the product’s shelf life.
Maintenance of Product Consistency
Food grade guar gum contributes to maintaining the consistency of processed foods, whether in terms of viscosity, texture or appearance. It helps food products maintain their form and function, providing a better consumer experience from start to finish.
Dosage and Usage Considerations in Formulation
To achieve the desired effects of moisture control in food products, it is important to use the correct dosage of guar gum powder. The amount of guar gum required will depend on the specific application and desired product characteristics.
Recommended Concentrations
Typically, guar gum is used in concentrations of the total formulation, depending on the food product. Higher concentrations may be needed in more moisture-sensitive products like frozen foods and dairy desserts.
Blending with Other Ingredients
Guar gum can also be blended with other hydrocolloids or ingredients to enhance its moisture control properties. For instance, combining guar gum with xanthan gum may provide synergistic effects, improving texture and moisture retention further.
Conclusion
In summary, guar gum powder plays a critical role in controlling moisture migration in processed foods, contributing to product stability, texture and shelf life. By binding water, forming moisture barriers and enhancing viscosity, guar gum helps ensure that food products remain in optimal condition from production through to consumption. As the food industry continues to evolve, the applications of guar gum are likely to expand, providing further innovations in food preservation and quality control.
FAQs About Guar Gum Powder
What is the primary function of guar gum in processed foods?
Guar gum primarily functions as a water-binding agent, helping to prevent moisture migration in processed foods, which improves texture and extends shelf life.
Can guar gum help in preventing sogginess in baked goods?
Yes, guar gum helps retain moisture in baked goods, preventing them from becoming soggy or overly dry, thus maintaining their desired texture.
How does guar gum compare to xanthan gum in food applications?
Guar gum has a higher water-binding capacity than xanthan gum, making it more effective in controlling moisture migration, especially in moisture-sensitive foods.
What is the recommended dosage of guar gum in food formulations?
Guar gum is typically used in concentrations ranging from 0.1% to 1.0%, depending on the food product and the desired moisture control effect.
Is guar gum safe for consumption in food products?
Yes, guar gum is recognized as safe for consumption when used within the recommended limits in food products. It is commonly used in a wide range of food applications, including baked goods, dairy and frozen foods.

CEO, Altrafine Gums
With over Four decades of expertise in the natural gums and hydrocolloids industry, Ajit Patel leads Altrafine Gums, a globally recognized manufacturer and exporter of Guar Gum Powder, Cassia Tora Powder (Cassia Gum Powder) and other Hydrocolloids. Under his visionary leadership, the company has built a strong reputation for quality, innovation, and reliability across the food, feed, pet feed, pharmaceutical, mining, oil drilling and cosmetic sectors.
Altrafine Gums has been serving global industries for decades with a focus on sustainable sourcing, research-driven production, and stringent quality control. Its wide product portfolio includes Guar Gum Powder, Cassia Tora Powder (Cassia Gum Powder) and other plant-based hydrocolloids that serve as key functional ingredients in diverse applications.
Ajit Patel’s commitment to excellence ensures that every product from Altrafine meets international standards of performance and purity. He is passionate about advancing the global reach of Indian hydrocolloids, fostering customer trust, and promoting eco-friendly, science-backed solutions that enhance product formulation and performance worldwide.








