Home / Cassia Tora Powder
Cassia Gum Powder Manufacturer
Cassia Tora L., (Cassia obtusifolia L.), Caesalpiniaceae, is a wild crop and grows in most parts of India as a weed. A natural gelling agent which has industrial and food applications is made commercially from the seed. Cassia grows in hot, wet, tropical climates both wild and commercially. Cassia is a tonic, carminative and stimulant. Cassia contains 1-2 % volatile cassia oil, which is mainly responsible for the spicy aroma and taste. The primary chemical constituents of Cassia include cinnamaldehyde, gum, tannins, mannitol, coumarins, and essential oils (aldehydes, eugenol, and pinene); it also contains sugars, resins, and mucilage, among other constituents. Cassia tora powder made from cassia tora seeds and cassia tora splits are some ancient natural ingredients. In India, cassia tora is used as a natural pesticide in organic farms. Roasted seeds are substituted for coffee, like tephrosia seeds. Cassia tora powder is most popularly used in the pet-food industry. It is mix with guar gum for use in mining and other industrial application. Cassia gum is the purified flour from the endosperm of the seeds of Cassia tora and Cassia obtusifolia which belong to the leguminosae family. Seeds of Cassia occidentalis are a naturally occurring contaminant in the source material. The intended use of Cassia gum is as thickener, emulsifier, foam stabilizer, moisture retention agent and/or texturizing agent in cheese, frozen dairy desserts and mixes, meat products and poultry products. Cassia gum is combined with other hydrocolloids such as Carrageenan or Xanthan gum, they will synergistically form gels with unique properties.
 Cassia Tora
Cassia Tora Cassia Tora Seeds
Cassia Tora Seeds Cassia Tora Splits
Cassia Tora Splits Cassia Tora Powder
Cassia Tora PowderChemical Structure and Physical Properties of Cassia Gum
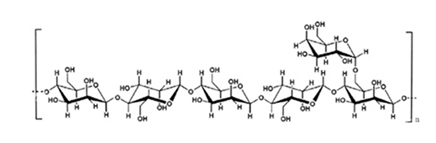
Cassia gum is comprised of at least 75% high molecular weight (approximately 200,000-300,000) polysaccharide consisting primarily of a linear chain of 1,4-β-D-mannopyranose units with 1,6 linked α- D-galactopyranose units. The ratio of mannose to galactose is about 5:1. The composition of saccharides is: mannose (77.2-78.9%), galactose (15.7-14.7%) and glucose (7.1-6.3%). Like most polysaccharides, the following formula applies: (C6H10O5)n.H2O. Cassia gum is related to carob bean gum, tara gum andguar gum in terms of structure and chemical properties.
Structural formula
Cassia Gum Regulatory Information
- Cassia gum is approved for use in Europe by the Commission Directive (EEC No. E 499) and is listed in the Annex of the Council Directive (70/524/EEC) as a stabilizer (thickening and gelling agent) in the manufacture of canned pet foods (for cats and dogs).
- It is also approved for use in Japan and is listed as a food additive in The Ministry of Health and Welfare Announcement No. 160 (10 August 1995).
- A panel of experts in the areas of toxicology, pharmacology and food science was assembled to review the safety of cassia gum for use as a thickening agent in human and pet foods in the United States.
- The available data on cassia gum and structurally related gums demonstrate a lack of toxic effects in animals. This review is the basis for the consideration of cassia gum as generally recognized as safe (GRAS) under conditions of its intended use as a thickening agent in human and pet foods.
- Abbreviations: FFDCA, Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act; GRAS, generally recognized as safe; NTP, National Toxicology Program; OECD, Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development; PADI, possible average daily intake
Regulatory Status
- United States TSCA
- Canada NDSL
- Korea ECL
- Australia AICS
- Europe EINECS
Gel (synergy) with Carrageenan or Xanthan Gum
Cassia gum forms firm, thermoplastic gels with carrageenan. As the level of cassia gum is increased, the gel strength of carrageenan solutions is also increase. Cassia gum and carrageenan gel is stable due to the excellent retorting stability of cassia gum. Cassia gum and xanthan gum, on their own, do not have the ability to form gels. But cassia gum combined with xanthan gum, aqueous dispersions of cassia gum form cohesive, elastic gels. As with carrageenan, cassia is more efficient at forming gels with xanthan gum than other galactomannans, enabling lower total hydrocolloid levels in finished formulations. This is due to the unique branched polysaccharide galactose/mannose structure of cassia gum. Cassia gum is manufactured from the endosperm of Senna obtusifolia or Cassia obtusifolia or Cassia Tora or Cassia Occidentalis). It is mainly used as a thickener and gelling agent in foods and pet foods. Cassia grows mainly in subtropical regions and is grows mostly wild and occasionally cultivated. Cassia Gum is comprised of at least 75% polysaccharide consisting primarily of a linear backbone chain of mannose with side galactose units The ratio of Mannose : Galactose is about 5: 1. Cassia gum, like LBG can form gels with other colloids like Carrageenan and Xanthan and is therefore used in the manufacture of gels in the food and pet food applications in combination of other colloids.
Translation of cassia Gum in different languages for the better understanding of our global clients:-| Catalan | Goma cassia |
| Croatian | Cassia guma |
| Danish | Cassiagummi |
| Dutch | Cassiapitmeel |
| Finnish | Cassiakumi |
| French | Gomme de cassia |
| German | Cassiakernmehl |
| Polish | Gumy cassia |
| Portuguese | Goma de cassia |
| Romanian | Guma de cassia |
| Slovenian | Guma cassia |
| Spanish | Goma cassia |
Splitting the Cassia Tora Seeds
The seed consists of an outer husk, an endosperm (cassia tora split) and the ovary or germ. Only the endosperm or split, which contains mainly polysaccharides, is used for the production of the cassia gum. Both husk and germ are removed in the de-husking and splitting process. The impact of the splitting procedure is that both husk and germ are loosened from the endosperm and made brittle by heating and can be removed in the subsequent purification procedure after pulverization. The split (endosperm), however, remains intact at these temperatures. Due to its much greater particle size, the split can be separated from husk and germ particles through a couple of physical cleaning steps. The splitting procedure starts with roasting of the seeds. All seeds are heated for several minutes. During the roasting process the endosperm (split) remains intact and flexible, while husk and germ, which are more sensitive to heat, become brittle. Mechanical stress pulverizes husk and germ and the powder is separated from the intact split by sieving. Remaining traces of husk and germ on the split particles are finally removed through a series of physical cleaning steps.
Method of Manufacturing Cassia Gum Powder
The seeds are dehusked and de-germed by milling and screening of the endosperm. Cassia Gum is high molecular weight (approximately 200,000 – 300,000) polysaccharides composed of galactomannans; the mannose:galactose ratio is about 5:1. Semi-refined Cassia gum normally containing detectable amounts of anthraquinones. The raw material seed is subject to different mechanical cleaning steps in order to remove other impurities, such as, farm waste, undeveloped seeds and stones. After cleaning raw material is subject to a de-husking and splitting process. Thermal and mechanical treatment removing husk and germ from the seeds resulting in splits. Finally the splits are ground to a uniform small particle size powder.
Chemical Structure and Physical Properties of Cassia Gum
- Cassia gum is hot water soluble and requires heating to fully solubilise and reach full viscosity in aqueous solutions.
- Cassia Gum is comprised of at least 75 % polysaccharide consisting primarily of a linear chain of 1,4-β-D-mannopyranose units with 1,6 linked α-D-alactopyranose units.
- The ratio of mannose to galactose is about 5:1.
- Cassia gum forms firm thermoplastic gels with carrageenan.
- Cassia gum and xanthan gum, on their own, do not have the ability to form gels. But cassia gum combined with xanthan gum, aqueous dispersions of cassia gum form cohesive, elastic gels.
- Cassia is known as one of the best gelling agent, thickening additives, emulsifying additives and stabilizing additives.
Cassia Gum Powder Number
- 1CAS No. of Cassia Gum Powder (Galactomannan) 11078-30-1
- 2INS NO for Cassia Gum Powder 427
- 3EINECS No. of Cassia Gum Powder 234-299-6
- 4EEC No. of Cassia Gum Powder E499
Cassia Tora Powder international listings
- 1Australia (AICS) Listed
- 2Korea KE – 17406
Gelling properties of refined cassia gum powder
Refined Cassia gum is a high number of galactose side chains prohibit the synergistic gelling effect with anionic polymers. As a result, a smaller amount of hydrocolloid blend containing cassia gum is needed in a food product to achieve the same effect as with carrageenan alone or blends of carrageenan with other related galactomannans.
Cassia Gum is mainly used as a
- Gelling Agent
- Thickener
- Emulsifier
- Stabiliser
- Bonding agent
FAQs - Cassia Tora Powder
Cassia Tora (Cassia Gum) Powder is derived from the seeds of the Cassia Tora plant. It is used as a thickening, gelling, and stabilizing agent in various industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics.
Cassia Tora Powder is primarily used in the food industry to improve texture and stability. It is also utilized in pet foods, pharmaceuticals, and personal care products for its thickening, gelling, and emulsifying properties.
The processing involves cleaning, de-husking, and milling the seeds of the Cassia plant. The endosperm is separated, purified, and ground into a fine powder to obtain Cassia Tora Powder.
Cassia Tora Powder enhances the texture, consistency, and stability of food products. It is an effective thickening and gelling agent that improves the shelf-life and quality of processed foods.
Yes, Cassia Tora Powder is safe for consumption when used within recommended guidelines. It is a natural product approved for use in food and pharmaceutical applications by various health authorities.
The typical shelf-life for Cassia Tora Powder is 2-3 years when stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture.
Yes, Cassia Tora Powder is gluten-free and can be used as a thickening agent in gluten-free products, making it suitable for individuals with gluten intolerance or celiac disease.
Key properties include high viscosity, excellent water-binding capacity, and strong gelling ability. These characteristics make Cassia Tora Powder valuable in various industrial applications.
Cassia Tora Powder offers advantages such as natural origin, cost-effectiveness, and versatility. It provides similar or superior thickening, gelling, and stabilizing properties compared to other agents and hydrocolloids.
We adhere to stringent quality control measures throughout the production process, including sourcing high-quality raw materials, implementing rigorous processing standards, and conducting thorough testing to ensure the purity and efficacy of our products.
We maintain consistent product quality through strict adherence to industry standards, regular quality audits, and continuous process improvements. Our products are tested at various stages of production to ensure they meet the required specifications.
We offer prompt delivery services to meet your needs. Depending on your location and order size, delivery times may vary, but we strive to ensure timely and efficient delivery of our products.
High-quality Cassia Tora Powder can be purchased from Altrafine Gums. We specialize in natural and organic industrial ingredients and adhere to stringent quality control measures to ensure product purity and efficacy.













